- +91 7829622525
- drvikashgoyal03@gmail.com
- Apollo Sugar Clinic, 2nd floor, Golf Course Road, Road, Street Number 48, DLF Phase 1, Gurugram, Haryana 122002
- Mon - Sat 09:30 AM - 05:00 PM
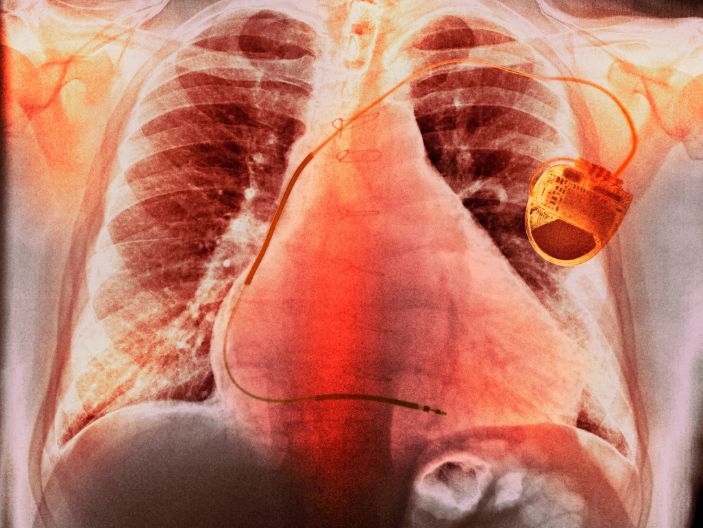
Pacemaker Implant
A pacemaker implantation is a surgical procedure performed to implant a small electronic device called a pacemaker into the chest or abdomen to help regulate abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). The pacemaker consists of a pulse generator and leads (thin wires) that are connected to the heart.
Once implanted, the pacemaker continuously monitors the heart's electrical activity. If it detects an abnormal rhythm or a pause in the heartbeat, it sends electrical impulses to stimulate the heart muscle, helping it maintain a regular and consistent rhythm. This helps prevent symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and shortness of breath that can occur due to irregular heartbeats.
Pacemaker implantation is a safe and effective treatment for various heart rhythm disorders, including bradycardia (a slow heartbeat), heart block, and certain types of arrhythmias. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and can significantly improve a patient's quality of life by ensuring that their heart beats at a healthy and consistent rate.