- +91 7829622525
- drvikashgoyal03@gmail.com
- Apollo Sugar Clinic, 2nd floor, Golf Course Road, Road, Street Number 48, DLF Phase 1, Gurugram, Haryana 122002
- Mon - Sat 09:30 AM - 05:00 PM
Arrhythmia Management
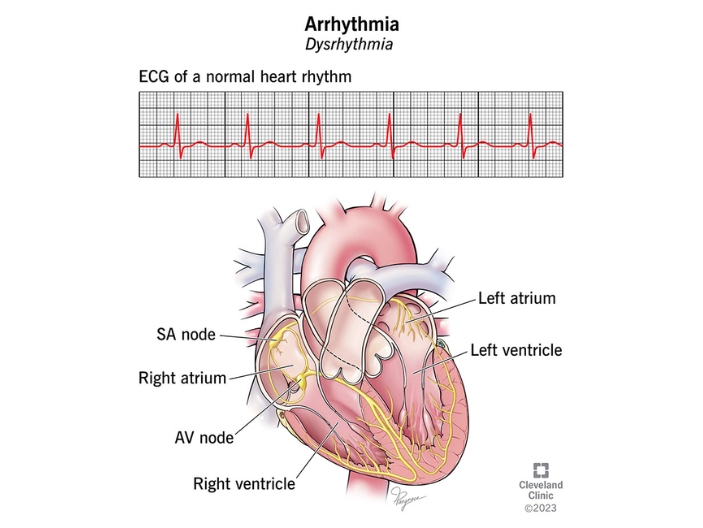
Arrhythmia management refers to the comprehensive approach to diagnosing, treating, and monitoring abnormal heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias. Arrhythmias can range from harmless to life-threatening and can cause symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Effective arrhythmia management typically involves the following components:
Dr. Rajakumari's proficiency in ureteral re-implantation, coupled with her compassionate patient care, establishes her as a trusted authority in nephrology and renal transplantation. For those seeking optimal outcomes in renal procedures, Dr. Rajakumari stands as a beacon of excellence in Delhi's medical landscape.
1. Diagnosis: Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the type and severity of the arrhythmia. This often involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), Holter monitor, event monitor, echocardiogram, stress test, electrophysiology study (EPS), and cardiac imaging studies
2. Risk assessment: Once diagnosed, the healthcare provider assesses the risk associated with the arrhythmia, including the potential for complications such as stroke, heart failure, or sudden cardiac arrest. This assessment helps guide treatment decisions and determine the appropriate level of monitoring and intervention.
3. Treatment: Treatment strategies for arrhythmia management aim to control symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include lifestyle modifications (e.g., avoiding triggers such as caffeine or stress), medication (e.g., antiarrhythmic drugs), catheter-based procedures (e.g., radiofrequency ablation), implantable devices (e.g., pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators), and in some cases, surgery.
4. Follow-up and monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are essential to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, adjust medications if necessary, and detect any changes or complications. Monitoring may include regular ECGs, Holter monitoring, event monitoring, or remote monitoring of implantable devices.
5. Lifestyle management: Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, managing stress, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol and caffeine intake can play a significant role in managing arrhythmias and reducing the risk of complications.
Overall, arrhythmia management requires a multidisciplinary approach involving cardiologists, electrophysiologists, cardiac nurses, and other healthcare professionals working together to tailor treatment plans to the individual needs of each patient. Through comprehensive care and ongoing monitoring, individuals with arrhythmias can achieve better symptom control, improve their quality of life, and reduce the risk of complications.